<< ---------------------------------------------------------------- >>
--- Last Modified: $= dv.current().file.mtime
<< ---------------------------------------------------------------- >>
EBS
IOPS: input/output per second high IO → lots of small, fast reads and writes
Throughput: data transfer rate to and from storage medium in MB/s
IOPS vs Throuput: IOPS measures the number of read and write operations per second, while throughput measures the number of bits read or written per second.
Bandwidth: measurement of the total possible speed of data movement along the network
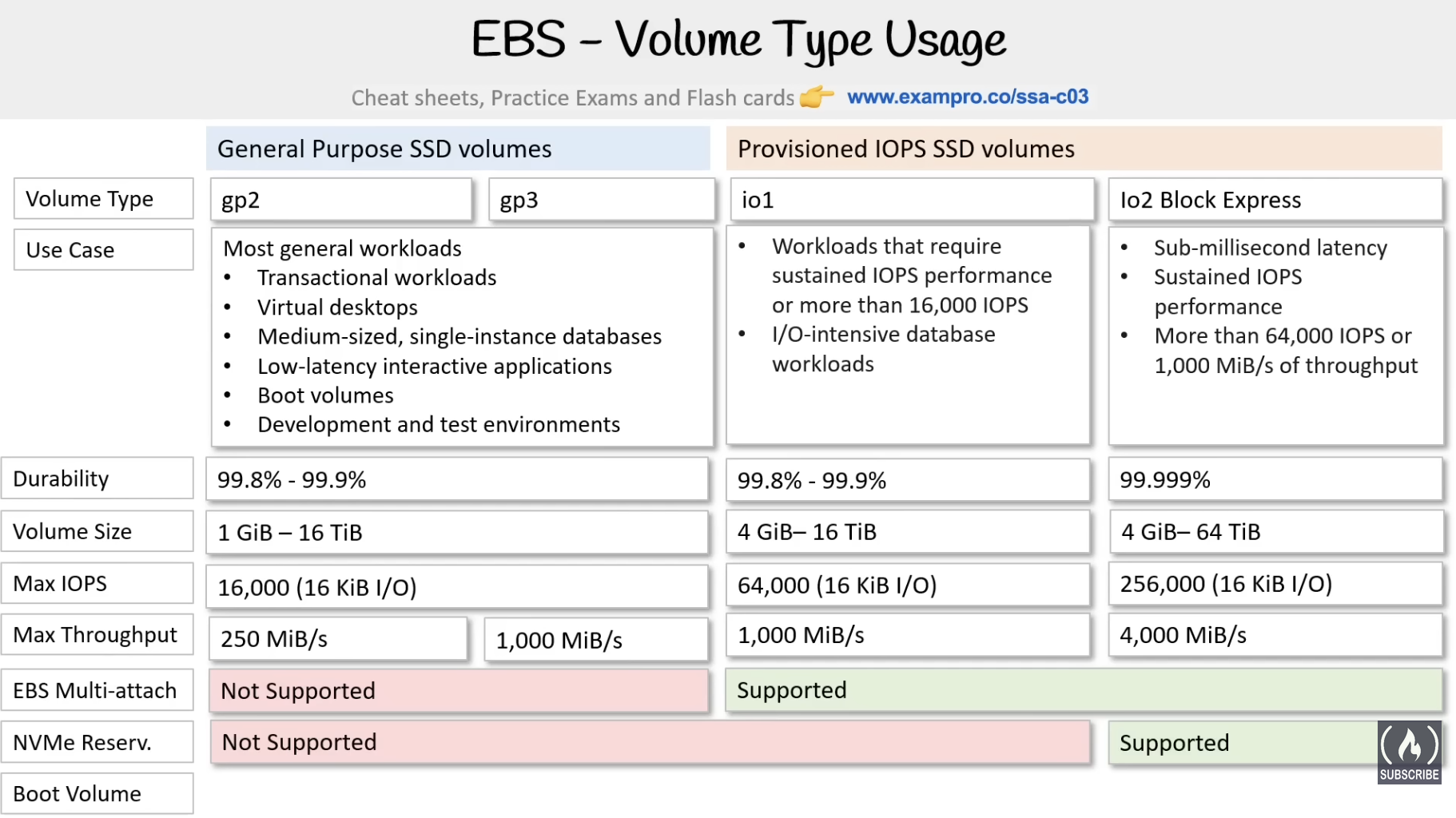
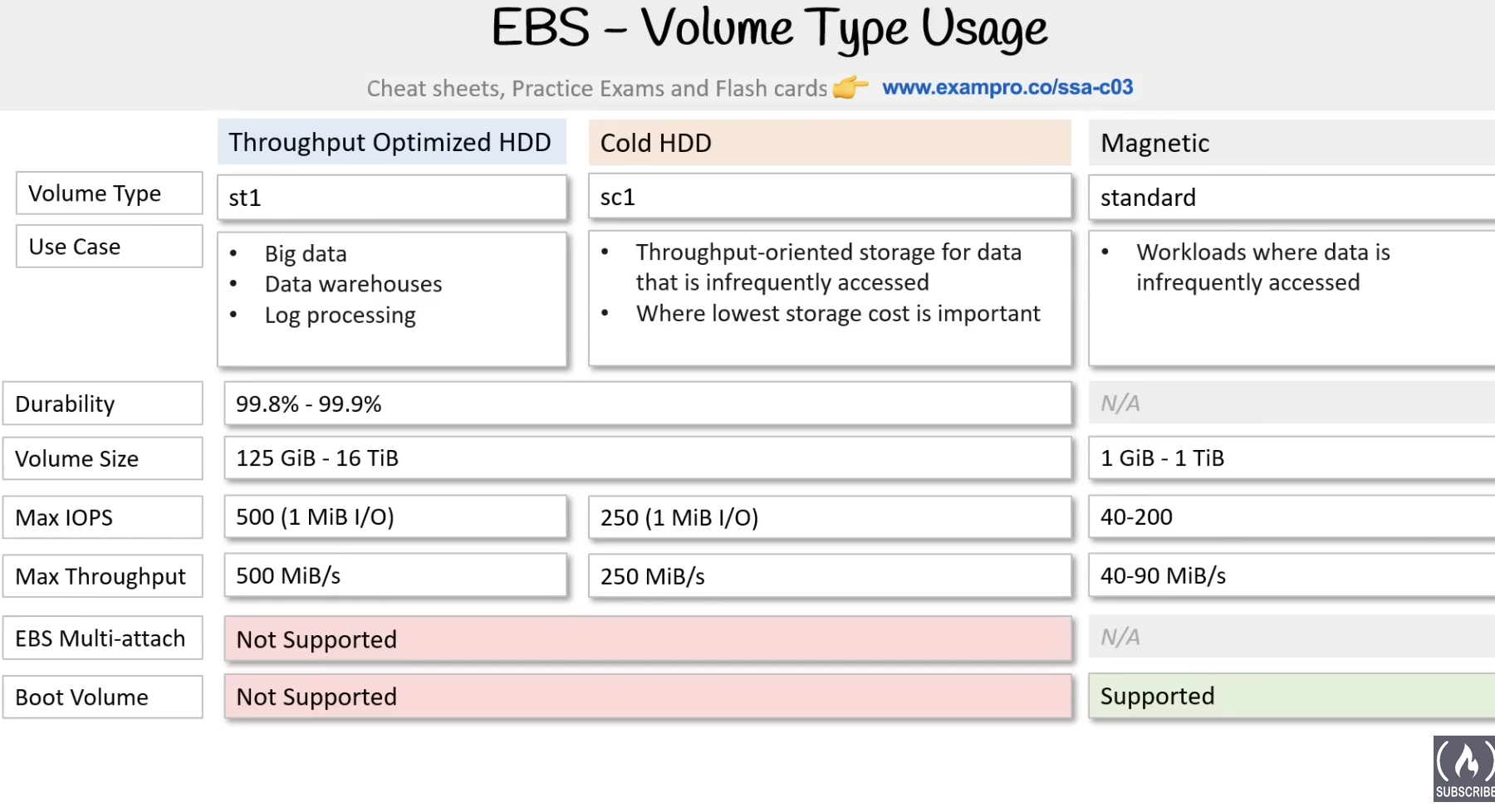
Types of Volumes
- General Purpose SSD(gp2) - general usage without specific reqs
- General Purpose SSD (gp3) - 20% lower cost per GB than gp2
- Provisioned IOPS SSD (IO1) - fast input output
- Provisioned IOPS SSD (io2) - mroe durable than io1 - all io2 volumes created after nov 23 are io2 block express, and the ones created before can be converted
- io2 Block Express - higher throughput and IOPS and support larger storage capacity
- Cold HDD (SC1) - lowest cost HDD for infrequent access
- Throughput Optimized HDD (st1) - Magnetic drive optimized for quick throughput
- Magnetic (Standard) - previous gen HDD
HDD
HDD RAID
Redundant Array of Independent Disks is a data storage virtual technology for magnetic disks(not magnetic tape) to improve fault tolerance. RAID combines multiple physical volumes into one logical group. Storing redundant data across disks. Since HDD has with mechanical parts and will result in wear HDD is more prone to failure
RAID 0 - Striping
- no redundancy; data is split across disks for high performance.
- increase speed and capacity but offers no fault tolerance
- minimum of 2 disks required RAID 1 - Mirroring
- Data is duplicated on two or more disks, offering high redundancy
- if one disk fails, data is still accessible from another
- requires at least 2 disks RAID 5 - Striping with Parity
- combines striping and parity for both speed and data protection
- can withstand the failure of one drive without data loss
- requires at least 3 disks
RAID 6 - Striping with Double Parity
- Raid 5 but with double parity, allowing it to survive the failure of two disks
- requires at least 4 disks RAID 10 (1+0)
- A combination of RAID 0 and 1, offering redundancy and increased performance
- min 4 disks