<< ---------------------------------------------------------------- >>
--- Last Modified: $= dv.current().file.mtime
EC2
<< ---------------------------------------------------------------- >>
Instance Types:
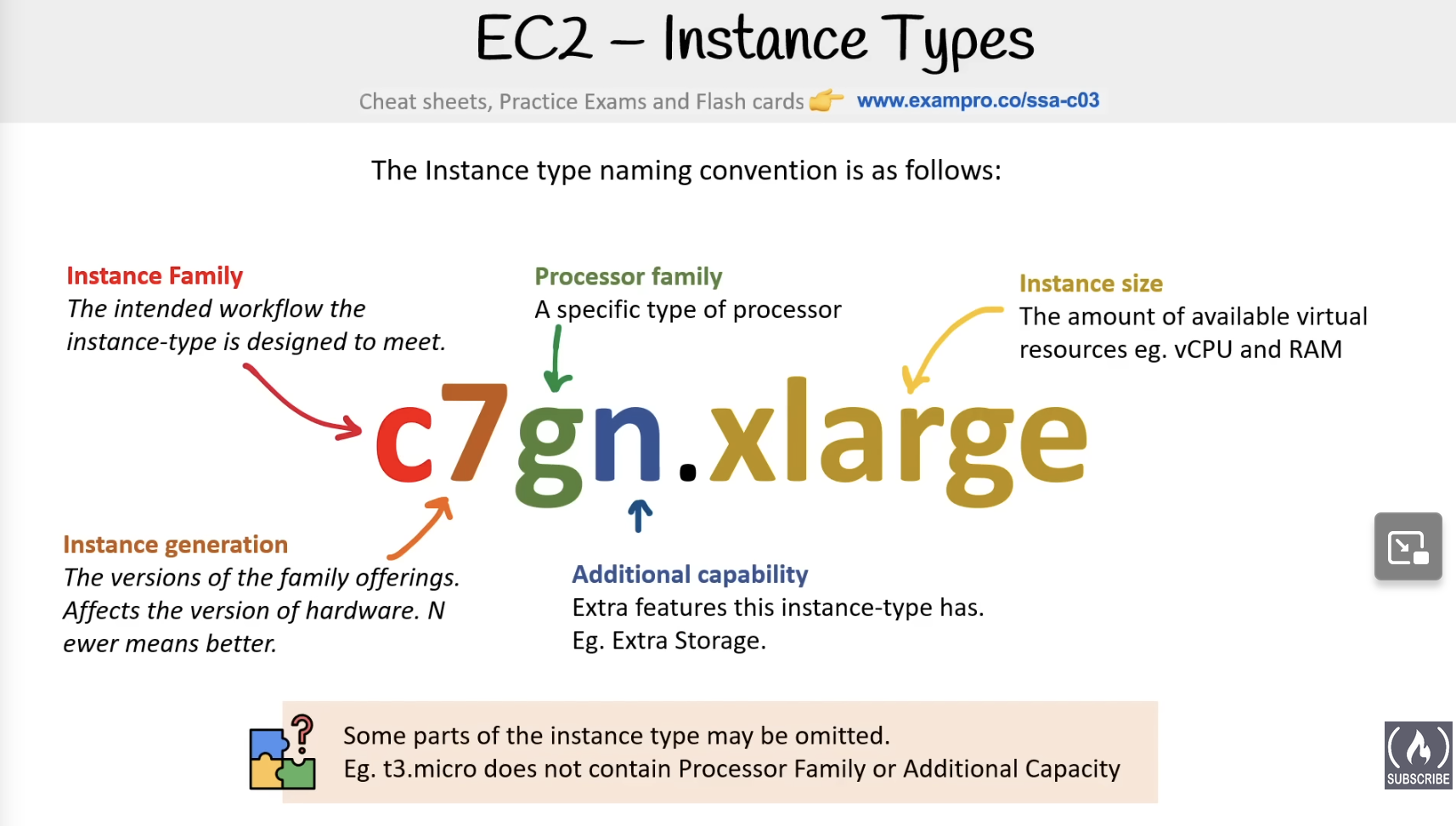
the first letter is instance family, the following number is instance generation, followed by processor family and then additional capability designations and the followed by instance size.
Types of Processors Used in AWS:
- Intel Xeon
- AMD EPYC
- NVIDIA GPU
- AWS Graviton Processors - ARM based
- Intel Habana Gaudi Processors - machine learning especialized
- Intel FPGAs - field programmable gate arrays for workloads that benefit from custom hardware accelrations
- AMD Xilinx - FPGA equivalent
- AWS Inferentia - high performance ML inference at low cost
- AWS Trainium - Training ML models
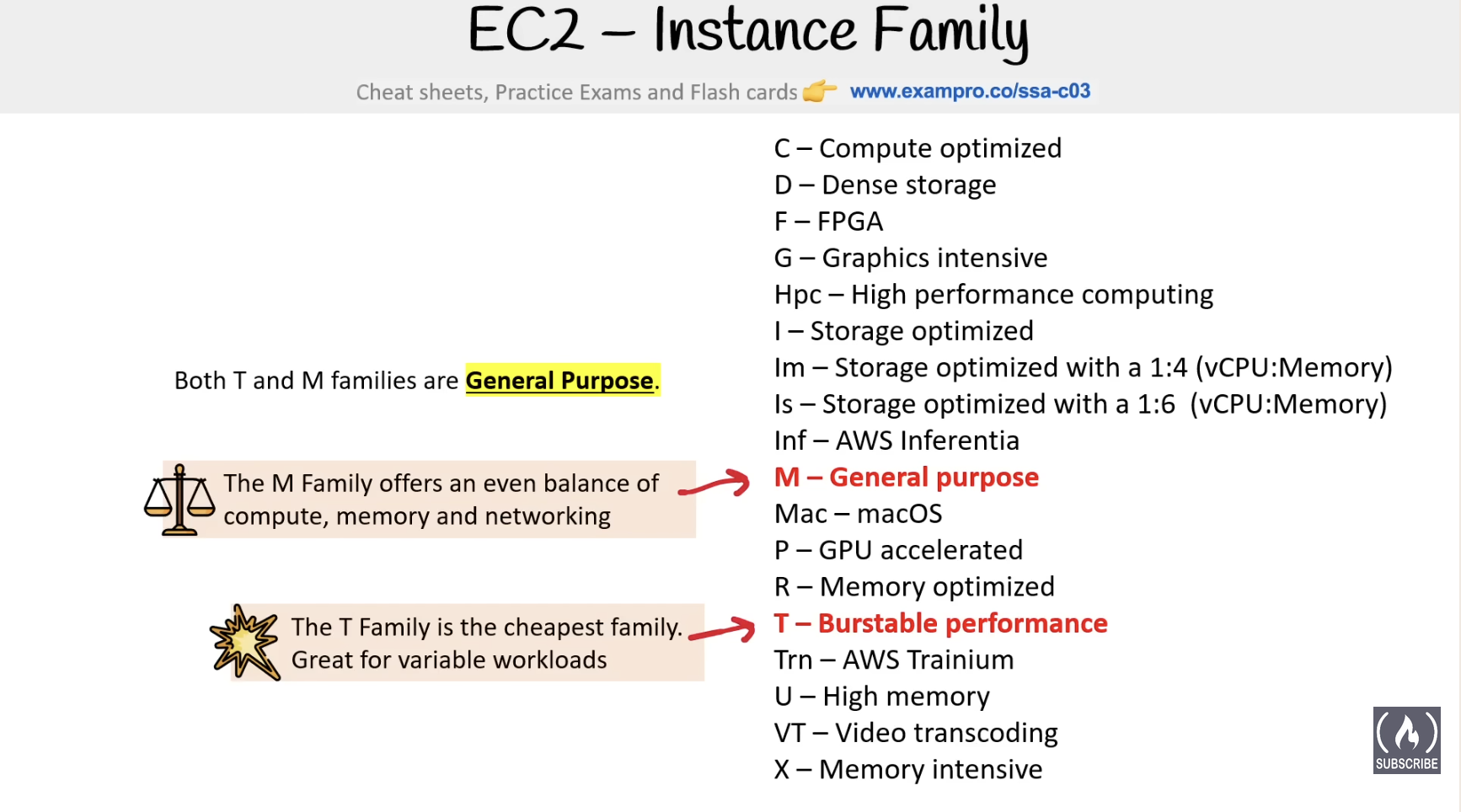
Instance Families:
- General Purpose: balance of compute, memory and networking resources, mostly for web servers and code repos.
- A1, T2, T3(xeon), T3a(amd epyc), T4g(gravitron - amazon arm), M4, M5, M6, Mac
- T line: Burstable instancess
- allows AWS customers to save money overall since they do not need to upgrade based on highest peak usage
- standard mode: baseline level of CPU performance with ability to burst using accumulated CPU credits.
- unlimited Mose: allows sustain high CPU performance for any period, with additional charges applied for usage beyond accumulated credits.
- Compute Optimized: ideal for compute bound applications that benefit from high performance processor - scientific modeling, dedicated gaming servers, ad server engines
- C5, C4, Cba, C5n, C6g, C6gn
- Memory Optimized: Fast performance for workloads that process large data sets in memory - in-memory caches, in-memory databases, real time big data analytics
- R4, R5, R5a, X1, X1e, High Memory, Z1d
- Accelerated Optimized: hardware accelrators or co-processors - machine learning, computational finance, seismic analysis, speech recognition
- P2, P3, P4, G3, G4ad, G4dn, F1, Inf1, VT1
- Storage Optimized: high, sequential read and write access to very large data sets on local storage - NoSQL, in-memory or transactional databased, data warehousing
- I3, I3en, D2, D3, D3en, H1
- I3, I3en, D2, D3, D3en, H1
Dedicated Hosts vs Dedicated Instances
Dedicated hosts are single-tenant EC2 instances designed to let you bring your own license based on machine characteristics.
The difference is that a deditaced instance has instance isolation while the host has physical server isolation, you have access to the sockets, cores, hostID etc…
Instance Launch Config
Cloud-Init
Industry standard multi-distribution method for cross-platform cloud instance initialization. Has meta-data, user-data(script that runs when the instance first boots up)), vendor-data and uses those to spin up an instance from an image.
IMDv1, IMDv2: The meta data of the device is available from the device itself through a specific endpiont. It has both ipv 4 & 6. You can get all information such as security groups, networking info etc from it.
V1 uses request response model, while v2 forces you to get a token first and then input the token as part of the request and response to be validated.
maybe have to know the IP address specifically for some reason??
IPV4 address Http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data
V2: Http://169.254.169.254/api/token Then you hit the previous endpoint and pass in the returning token as a part of the X-aws-ec2-metadata-token and
AMI - Amazon Machine Image
an AMI holds the following:
- a template for the root volume for the instance(EBS snapshot or instance store template) - OS, application server and applications
- Launch Permissions that control which AWS accounts can use the AMI
- A block device mapping that specifies the volumes to attach to the instance when its launched
AMIs are REGION SPECIFIC.
they help you keep incremental changes to your OS, app code and system packages.
Using SYstems Manager Automation you can routinely patch your AMIs with security updates and bake those AMIs.
AMIs are used withh Launch Configurations or Launch Template to manage AMI revisions. You can Copy AMIs directly into different regions and/or encrypt them You can store AMIs into S3 buckets and then copy the AMI from one AWS partition to another.
Access & SSH
Hostnames
a unique name in your network to identify a machine via DNS
changing the hostname could be necessary in specific use cases where software is expecting a very specific name when building micro-services such as using Service Meshes might have you change hostnames.
Two types: legacy, used only when launching IPv4 ip-ipaddresshere.ec2.internal if not in us east 1 followed by region.compute.internal instead if dual stack: ec2-instance-id.ec2.internal, same thing with the region.
Instance Profile
Its an IAM role that the instance assumes so you dont have to manually input long lived AWS credentials things into the environment. Uses STS assume role.
you can do that either before or after boot, if after boot have to do a hard reset do to eventual consistency
Ways to Connect
- SSH client
- EC2 instance connect
- short lived SSH keys controlled by IAM policies - only works with linux
- sessions manager
- linux or window via a reverse connection
- no need to open ports
- supports audit trail of logins
- Fleet Manager Remote Desktop
- connect to windows machine using RDP within the web-browser
- EC2 Serial console
- establish a serial connection giving you direct access to underlying hardware for troubleshooting hardware - has to be build on the Nitro system - which is an aws hypervisor
ASG - Auto Scaling Groups
Any services that uses EC2 underneath can be used for this. Except for Fargate since it scales itself and is a fully managed service. (might be using ASG under the hood )
auto scaling can occur when:
- capacity settings - set the expected range of capacity
- manual scaling
- you input the min-size, max-size and desired capacity.
- this is considered manual scaling since you have to manually input those 3 numbers
- manual scaling
- Health Check requirements
- Scaling Policies
- Dynamic Scaling Policies - has three adjustment types: ChangeInCapacity, ExactCapacity, PercentChangeInCapacity - based on CloudWatch alarms
- Simple Scaling: simply change capacity in either direction by a certain amount when a CloudWatch alarm is triggered.
- Step Scaling: change capacity in either direction by a certain amount at different thresholds(steps) when a CloutWatch alarm is repeatedly triggered
- Target Tracking Scaling - scales based on a target metric value - for example averageCPUUtilization, AveragenetworkUtilization etc…
- Predictive Scaling: analyzing historical load data to detect daily or weekly patterns in traffic flows.
- Dynamic Scaling Policies - has three adjustment types: ChangeInCapacity, ExactCapacity, PercentChangeInCapacity - based on CloudWatch alarms
Physical Placement Groups & Tenancy
EC2 Placement Groups
lets you choose the logical placement of your instances to optimize for communication, performance, or durability. Placement groups are free.
- cluster
- close together inside AZ
- low latency network performance for tightly coupled node-to-node communication
- good for high performance computing
- cannot be multi AZ
- partition
- spreads instances across logical partitions
- each partition does not share the underlying hardware (rack per partition)
- for large distributed and replicated workloads(hadoop, cassandra, kafka)
- spread
- each instance on a different rack
- when critical instance should be kept separate from each other
- you can spread a max of 7 instances. spreads can be multi-az
EC2 Tenancy
Three levels:
- Dedicated Host: your server lives here and you have control of the physical attributes
- Dedicated Instance: your servers always lives at a specific spot on a specific server rack
- Default: your instance is in the same spot until reboot, then it can change.
Pricing
Pricing Models
On-Demand, Spot, Reserved, Dedicated
- On-Demand:
- pay as you go. Charged by the second or the hour.
- on-demand is good for workloads that are short-term, spiky, unpredictable. When you have a new app for dev or running an experiment.
- Reserved Instances(RI):
- For apps with a Steady-state, predictable usage or require reserved capacity.
- A guaranteed commitment to use AWS resources for a period of time → about 70% saving in price but in a contract.
- Term: contract length could be from 1 to 3 years
- Class
- Standard: up to 75% saving, can modify Reserved Instance attributes.
- Convertible: up to 54% reduced pricing compared to on demand. You can exchange RI based on RI attributes if greater or equal in value.
- Payment option:
- all upfront
- partial upfront
- no upfront
- RI Attributes (instance attributes)
- are limited based on calss offering and can affect final price
- Instance type: m4.large
- region
- Regional and Zonal RI
- Regional: purchase for a zone
- does not reserve capacity
- usage in any AZ in the region
- you can queue purchases for regional RI
- instance size flexibility: it applies to instances within the family regardless of size
- Zonal: purchase for availability zone
- reserves capcity in the specified availability zone
- discount only for the availability zone
- no instance size flexibility
- you can queue purchases
- tenancy
- platform(windows, linux)
- Limits:
- per month
- you can only do 20 regional per region and 20 zonal per AZ
- per month
- you can reserve EC2 spots but you will be billed for it even if the machine is not running
- You can sell them on the RI marketplace if you are not using the entirety of your commitment.
- Spot Instances:
- AWS has unused compute capacity that they want to maximize the utility of their idle servers.
- Designed for apps with flexible start and end times.
- AWS batch is an easy and convenient way to use spot pricing.
- Dedicated:
- Designed to help meet regulatory requirements. When you have strict server-bound licensing that wont support multi-tenancy or cloud deployments you use dedicated hosts.
Savings Plan
similar discounts to reserved instances but simplifies the purchasing process.
3 types:
- Compute savings Plan:
- automatically apply to EC2 usage
- EC2 Instance Savings Plan:
- reduces costs on selected isntance family in the region, gives flexibility to change instance within a family in the region
- SageMaker Savings Plan:
- same thing but for SageMaker(ML stuff that uses EC2 under the hood)
AWS Compute Optimizer
Analyzes the current configuration of you aws compute resources, and their utilization metrics from amazon CloudWatch over a period of the last 14 days.