<< ---------------------------------------------------------------- >>
Networking Basic
<< ---------------------------------------------------------------- >>
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IPvYjXCsTg8
Internet is basically a collection of computer networks.
How did the internet start?
Basically they had multiple sites for development of satellites and needed them to communicate with each other. They were at MIT, UCLA, Stanford, Utah. the computers used TCP(Transmission Control Protocol) to communicate with each other. And eventually enough computers got added and it lead to the creation of WWW(world wide web).
Network Protocols
basically a set of rules (defined by the internet society) that dictate how data is sent over the internet. TCP(Transmission Control Protocol) is one. like for example for a certain protocol the network has to make sure that 100% of the data is delivered. for another, it might be fine to drop a few bits and pieces.
How is data transfer anyway
Data is always transferred in packets to ensure that large data sets are able to be transferred.
IP(Internet Protocol)
All devices that are on the internet have an IP address. All IP addresses have a x.x.x.x format each x being from 0 to 255.
How internet is organized locally
LAN(local area network)
just connecting computers locally. Like ethernet to each other etc…
MAN(metropolitan area network)
across a city
WAN(wide area network)
across countries, usually by fiber optic cables. SONET: Synchronous optical networking: carries the data using fiber optic, so it covers larger distances Frame relay: How we connect LAN to the internet.
basically multiple LANs are connected to each other using MAN which are connected using WANs
Modems, Routers
Modems: used to convert digital signals to analog signals and vice versa. Router: Device that routes the data packets based on the IP Addresses.
Topologies(how computers are connected)
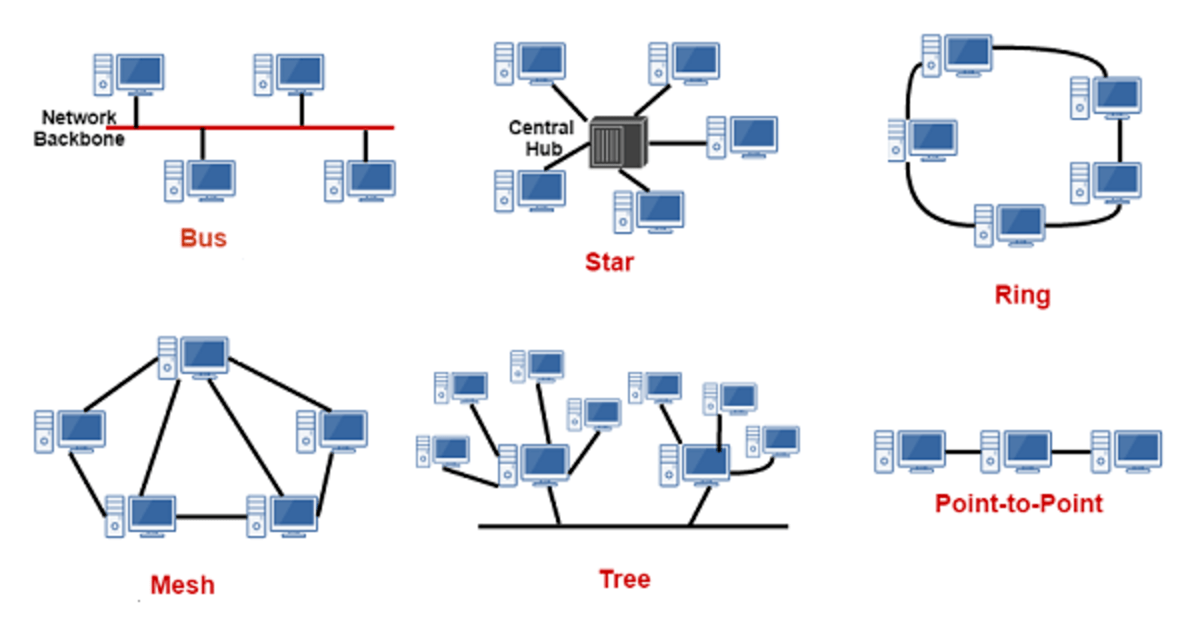
Bus
If the line breaks all the downstreams cannot be connected to the internet, and also since its only one line, only one can transmit data at a time.
Ring
if one cable breaks the entire system is down. also a lot of unnecessary calls are being made if they’re not directly next to each other.
Mesh
since all computers are connected to each other, it gets expensive, and will have scalability issues.
Star
If the central device fails the network will go down.
Structure of Network
Networking Devices
Repeater
Its in the Physical Layer, and its job is to regenerate the signal over the network at its original strength(it doesn’t amplify it).
Hub
A multi-port repeater(star topology) Types: 1. Active hub 2. Passive hub
Bridge
In the 02-Data Link Layer. A type of repeater with more functionality: it can filter out content by reading MAC addresses from the source
Switch
A multi-port bridge, also at the 02-Data Link Layer.
Router
Gateway
A passage that connects 2 networks together.
Brouter
Bridge and a router combined.
Cookies
Basically remembers States from a session. HTTP is stateless, so we have to find a way to save the states. This happens using Cookies, its a unique STRING that is stored on the browser. 1. The first time the application is visited, it sets a cookie. 2. After that every time a request is send, it also sends a cookie in the header of that request. 3. The Backend will have a Database that stores the cookies and their States, and the server will be able to recognize which session it belonged to. It can be abused tho to track other activities to show ads and things like that.
Third Party Cookies
Cookies set for URLs that we do not visit.