<< ---------------------------------------------------------------- >>
IP(Internet Protocol)
<< ---------------------------------------------------------------- >>
IP Address
Your ISP(internet service provider) gives you a modem. That modem has a global IP Address. All the devices that are going to be connected to that modem will have the same IP address to the outside world.
The modem will also give IP addresses to the devices connected to it(local IP addresses) using DHCP(dynamic host configuration protocol).
The device will make a request to the modem, the modem sends it to the ISP and the ISP will send it to the internet. Once the request comes back from the ISP to the router, the router reads it and decides which device to send the response to using NAT(Network Access Translator).
IP address decides which DEVICE we will send the data too, but what will decide which application in that device consumes the response?, The PORT decides that.
IPv4
32 bit numbers, 4 - words The first 3 numbers are the network address(they indicate the subnets), and the last one is the host address.
Subnet Masking(Netmask)
it masks the network part of the IP address(the first 3), and just give us the host part. 12.0.0.0/32 so the first 32 bits(3 digits) are fixed and we can only use the last digit.
in each network the first 2 and last ip addresses are reserved. last one(.255) is the broadcast address, first one (.0) is the network address and second one (.1) is the default gateway adderss(where the router lives) so V4 has 253 available addresses for each network.
Reserved Addresses
localhost: 127.0.0.1 loopback addresses
Classes

Class A for example since it has so many networks based on a single address is usually given to really big companies with very big networks like IBM or ATT Classes D and E are not accessible and the 127.0.0.0(which is a class A IP address is the reserved local address-this inludes all addresses in its 255.0.0.0 mask as well-)
Running out of IP addresses:
RFC 1918:
basically an agreed upon standard that sets aside a number of IP addresses as private IP addresses. Meaning that they don’t connect you to the internet and are only accessible by local network. These addresses include:
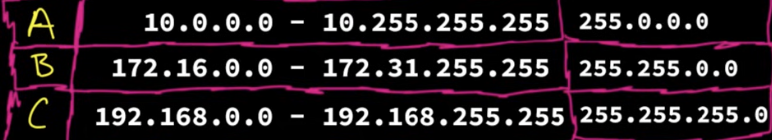
NAT(Network Access Translator) is what translates this local address into the global public address at the 03-Network Layer and routers.
We still ran out of IP addresses tho so here comes:
IPv6:
128 bit numbers, it is not backwards compatible. ISPS would have to shift a lot of hardware work to adopt it, which is why it is not widely adopted.
PORTs
Ports are 16 bit numbers so a total of 2^16 ports in a computer.
Ports 0-1023 are reserved ports so you cant put custom applications on them.
1024-49152 are reserved for applications. you can use the remaining ports.
Packets
Header is 20 bytes. it includes IP version, length, identification, flags(TCP flags), TTL(time to live). TTL: basically if a packet after a certain period of time hasn’t reached its destination, it will be dropped from the network.